MONJUVI is targeted immunotherapy that effectively binds to CD191
- MONJUVI is an Fc-modified monoclonal antibody that binds to the CD19 antigen expressed on the surface of pre-B and mature B lymphocytes and in several B-cell malignancies, including DLBCL
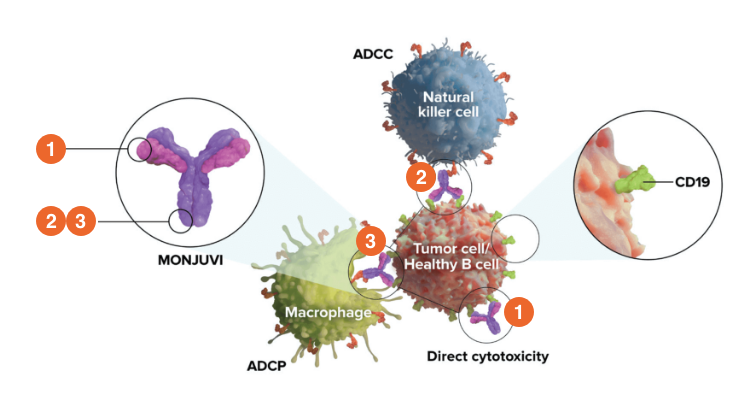
Upon binding to CD19, tafasitamab-cxix mediates B-cell lysis through:
- Apoptosis
- Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP)
Fc=fragment crystallizable.
In studies conducted in vitro in DLBCL tumor cells, tafasitamab-cxix, in combination with lenalidomide, resulted in increased ADCC activity compared to tafasitamab-cxix or lenalidomide alone1
MONJUVI Mechanism of Action Video
Indications & Usage
MONJUVI (tafasitamab-cxix), in combination with lenalidomide, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low grade lymphoma, and who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
Important Safety Information
Contraindications
None.
Warnings and Precautions
Infusion-Related Reactions
MONJUVI can cause infusion-related reactions (IRRs). In L-MIND, infusion-related reactions occurred in 6% of the 81 patients. Eighty percent of infusion-related reactions occurred during cycle 1 or 2. Signs and symptoms included fever, chills, rash, flushing, dyspnea, and hypertension. These reactions were managed with temporary interruption of the infusion and/or with supportive medication. Premedicate patients prior to starting MONJUVI infusion. Monitor patients frequently during infusion. Based on the severity of the infusion-related reaction, interrupt or discontinue MONJUVI. Institute appropriate medical management.
Myelosuppression
MONJUVI can cause serious or severe myelosuppression, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. In L-MIND, Grade 3 neutropenia occurred in 25% of patients, thrombocytopenia in 12%, and anemia in 7%. Grade 4 neutropenia occurred in 25% and thrombocytopenia in 6%. Neutropenia led to treatment discontinuation in 3.7% of patients.
Monitor complete blood counts (CBC) prior to administration of each treatment cycle and throughout treatment. Monitor patients with neutropenia for signs of infection. Consider granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) administration. Withhold MONJUVI based on the severity of the adverse reaction. Refer to the lenalidomide prescribing information for dosage modifications.
Infections
Fatal and serious infections, including opportunistic infections, occurred in patients during treatment with MONJUVI and following the last dose.
In L-MIND, 73% of the 81 patients developed an infection. The most frequent infections were respiratory tract infection (24%), urinary tract infection (17%), bronchitis (16%), nasopharyngitis (10%) and pneumonia (10%). Grade 3 or higher infection occurred in 30% of the 81 patients. The most frequent grade 3 or higher infection was pneumonia (7%). Infection-related deaths were reported in 2.5% of the 817nbsp;patients.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection and manage infections as appropriate.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, MONJUVI may cause fetal B-cell depletion when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise women of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with MONJUVI and for at least 3 months after the last dose.
MONJUVI is initially administered in combination with lenalidomide. The combination of MONJUVI with lenalidomide is contraindicated in pregnant women because lenalidomide can cause birth defects and death of the unborn child. Refer to the lenalidomide prescribing information on use during pregnancy.
Adverse Reactions
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 52% of patients who received MONJUVI. Serious adverse reactions in ≥6% of patients included infections (26%), including pneumonia (7%), and febrile neutropenia (6%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 5% of patients who received MONJUVI, including cerebrovascular accident (1.2%), respiratory failure (1.2%), progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (1.2%) and sudden death (1.2%).
Permanent discontinuation of MONJUVI or lenalidomide due to an adverse reaction occurred in 25% of patients and permanent discontinuation of MONJUVI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 15%. The most frequent adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of MONJUVI were infections (5%), nervous system disorders (2.5%), respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders (2.5%).
Dosage interruptions of MONJUVI or lenalidomide due to an adverse reaction occurred in 69% of patients and dosage interruption of MONJUVI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 65%. The most frequent adverse reactions which required a dosage interruption of MONJUVI were blood and lymphatic system disorders (41%), and infections (27%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were neutropenia (51%), fatigue (38%), anemia (36%), diarrhea (36%), thrombocytopenia (31%), cough (26%), pyrexia (24%), peripheral edema (24%), respiratory tract infection (24%), and decreased appetite (22%).
Please see the full Prescribing Information for additional Important Safety Information.

